A solid-state drive, sometimes known as an SSD, is a computer storage device. On solid-state flash memory, this non-volatile storage medium holds permanent data. Traditional hard disc drives (HDDs) are being phased out of computers favouring SSDs, which perform the same essential duties. SSDs, on the other hand, are considerably are faster and help in faster system bootup, decrease loading time for apps, and transfer files at higher speed.
A hard disc drive (HDD) uses magnets to read and write data. A typical hard drive has a spinning disc with a read/write head mounted on a mechanical arm known as an actuator. Mechanical failures can occur as a result of magnetic characteristics.
What are SSDs Used For?
Business SSDs are frequently used by companies that operate with large volumes of data (such as development environments or data analysis), as access times and file transfer rates are crucial.
Gaming PCs have always pushed the boundaries of current computer technologies, necessitating the purchase of costly equipment for gaming performance. This is especially true in storage because current blockbuster games are continually loading and writing files (e.g. textures, maps, levels, characters).
SSDs use little power, resulting in longer battery life in laptops and tablets. SSDs are also shock resistant, which means data loss is less likely when mobile devices are dropped.
In order to take care of client PCs, enterprise servers require SSDsfor fast readings and writes.
SATA Hard Drives
SATA is a hard drive interface that allows you to read and write data to and from your hard drive (HDD or SSD) and your computer. These devices, sometimes known as serial ATAs, are often found in desktop computers, laptops, servers, and game consoles. SATA drives were inserted in the PlayStation 3 and 4 and the Xbox 360 and One, by Sony and Microsoft, respectively.

Features
SATA hard drives come in various sizes depending on their intended usage. 4 inches wide, 1.03 inches tall, and 5.79 inches long are the dimensions of desktop sata hard drive. They’re commonly referred to as 3.5-inch hard discs.
For laptops, a smaller version of the desktop SATA drive is available. SATA hard discs for laptop computers are typically 2.7 inches broad, 0.37 inches in height, and 3.96 inches long.
There are several benefits to utilizing a SATA hard disc. They’re noted for their high transmission speeds, large capacity, compatibility, and affordability.
SATA devices, as previously stated, can write data at a rate of around 600 megabytes per second. Modern SATA hard drives are available in capacities ranging from 500 GB to 16 TB, ranging from $50 to $500 depending on storage capacity and features.
Compatibility is another benefit of utilizing a sata hard drive. SATA devices may be utilized in practically any arrangement and from various vendors (including Apple). Furthermore, SATA hard drives may be hot-swapped.
Hot-swapping is known as adding or removing a hard disc while the device is still functioning. This isn’t something you’ll discover on every hard disc!
Parallel ATA (PATA) interface hard drives were the standard storage method in the computer industry before SATA drives arrived. These devices, first introduced in 1986, were slower and bigger than their replacement, the SATA hard disc.
PATA drives write at speeds ranging from 66 to 133 megabytes per second. On the other hand, SATA drives write at a rate of 600 megabytes per second. That’s a six-fold increase in speed—a big improvement!
The Serial ATA Working Group, a non-profit organization, made up of the best brains from the world’s biggest computer corporations, produced the first SATA drive specifications in 2000. The Serial ATA International Organization has developed numerous generations of SATA technology since then, and the device is still important today as it was in 2000.
What is mSATA?
mSATA is a tiny form factor flash storage device that works like a hard disc drive in a host computer system. The mSATA drive must be connected to a particular connection on the host system. The mSATA may be used to store operating systems, programmes, and other data, just like conventional flash storage devices.
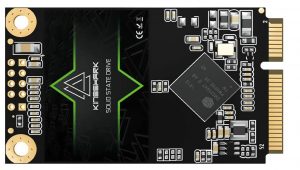
Features
The mSATA form factor is defined by both the SATA-IO Group and JEDEC. With 50.8mm x 29.85mm, the mSATA SSD drive packs a lot of storage into a compact package. Depending on the model, it can handle one or all three SATA interface specifications, ranging from 1.5 Gbits/sec to 6.0 Gbits/sec.
The mSATA provides a solution for each application, whether industrial or commercial.
Another benefit of Industrial mSATA is its extended lifespan. In many cases, the life cycles of industrial flash storage devices exceed five years. Because manufacturing units are built using the same Bill-Of-Material for many years, only one certification is necessary.
All of the benefits of the Industrial mSATA come at a premium cost. The memory and controller technology required to achieve the stringent requirements is costly. As a result, the Industrial mSATA is much more costly than the standard mSATA.
Cactus provides our Commercial Grade mSATA, based on lower-cost MLC NAND flash memory, for applications that require a cost-effective solution for less demanding workloads.
Initially, this SSD was available in capacities ranging from 32GB to 64GB, clearly insufficient for storing information. This implies that users must prepare a hard drive to store files while utilizing this SSD to reduce the time it takes for the system and apps to load.
However, owing to the efforts of a few businesses, mSATA SSD capacity has already reached 1TB (like Samsung Electronics 850 EVO mSATA SSD).
When purchasing an SSD for our devices, efficiency is the most critical consideration. Disk performance is directly connected to simultaneous read and write speeds.
Disk access patterns are what they are. To be more exact, they refer to the quantity of data a disc can retrieve and write in MB per second. SATA III is used in today’s mSATA SSDs, which can achieve speeds up to 6Gb/s.
You may use several trusted programs, such as MiniTool Partition Wizard, to evaluate the performance of the disc you’ve brought. The penultimate section of this essay is a full explanation of how to test drive using this tool.
M.2 NGFF
The M.2 specification defines internal expansion cards for PC mainboards and laptop computers. M.2 was created to replace the mSATA interface and was initially launched in 2012 by Intel under the name Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF).

Features
Additionally, M.2 NGFF SSD is more versatile in terms of usage and interface variety since it can transmit SATA signals and USB and PCIe data. Extended functionality is conceivable as a result, such as using WLAN, Bluetooth, GPS, or NFC cards.
The rectangular form of M.2 cards. They have a plug connector strip on the front side and a centred semicircular recess on the rear side. Components can be put on both the top and bottom sides of the card.
The card must be mounted in the recess, which may be slid into the proper port on the board and secured with a screw.
The form factor of an M.2 NGFF SSD module determines its size. The form factor specifies the width in millimetres divided by the length in millimetres.
The form factor 2260, for example, denotes a card with a width of 22 mm and a length of 60 mm. The most extended components are 110 millimetres long.
Final Lines
If you’re a gamer, developer, or ordinary user looking to upgrade your laptop or desktop’s hard drive, a SATA3 is a way to go.
Users having a mSATA or M.2 connection on their laptop or ultrabook who don’t wish to replace their present HDD can purchase an mSATA or M.2 SSD. Because two connections have replaced mSATA connectors, the availability of mSATA SSDs is restricted.
If your PC or laptop enable it, enthusiasts and users who make and render films in 4K quality or conduct other jobs that need a lot of disc I/O should consider an NVMe SSD.

Hi, this is Masab, the Founder of PC Building Lab. I’m a PC enthusiast who loves to share the prior knowledge and experience that I have with computers. Well, troubleshooting computers is in my DNA, what else I could say….